The Definitive Guide to 5G, LTE Network, UMTS, and GSM KPI Categories and How They Affect Your Quality of Service (QoS).
Before we go into the KPI and categories, let’s first define what quality of service means:
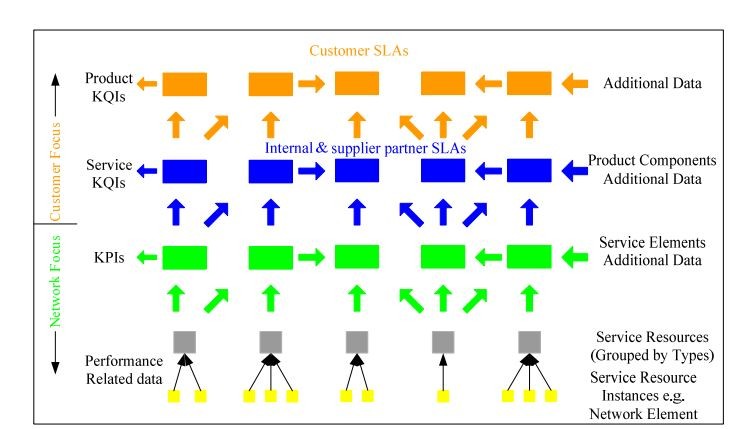
Quality of Service (QoS) defines the network quality in quantitative network performance parameters named Key Performance Indicators (KPI).
keywords: quality of service, quantitative
# Introduction – What are KPIs?
keywords: what is a KPI, measurement of quality, service quality
KPIs are key performance indicators. They are measurements of quality and service quality.
A KPI is a key performance indicator that measures the effectiveness of a process or system. It is a measurable value that can be used to judge the success of an organization, product, or service.
KPIs are often used to measure the overall performance of a network and its services. The service experienced by end users is measured using some performance indicators (PIs) that are aggregated to form a KPI. According to the 3rd generation partnership project (3GPP) standard, see the main KPIs that directly influence network performance and end-user experience:
# Accessibility
keywords: how to measure customer accessibility, customer satisfaction with accessibility One of the most important things for any company is to make sure that their customer is satisfied. One way to measure customer satisfaction is by looking at how accessible the radio network is.
Use case description: In providing end-user services to wireless end-users, the first step is to get access to the wireless service. First, after access to the service has been performed, the service can be used. In the case of the LTE network-measure the impact of the E-UTRAN on end-users service accessibility, used for this KPI: E-RAB.
# Retainability
keywords: how to measure customer retainability, retention rate)
Retainability is a measure of how customers are able to stay in your network without interruption. If a user is interrupted often while using a service, or if the service is aborted during use. In the case of the LTE network-measure the impact of the E-UTRAN on end-users service accessibility, used for this KPI: E-RAB.
# Integrity
keywords: how to measure integrity, what does integrity mean)
Integrity is a word that is often used in the workplace and in everyday life. But what does it really mean?
The Oxford Dictionary defines integrity as “the quality of being honest and having strong moral principles; moral uprightness”. In our case integrity, indicates the quality of service that CSP is offering. In the case of the 5G network, end-to-end network latency KPI is used to measure the overall packet transmission, transfer latency, and packet discard rate of 5G networks and networks in general.
In the case of measuring the impact of RTT (round-trip time) end-to-end latency of UE IP packets transmitted from UE to the N6 interface in the 5G network, the N6 interface is the reference point between UPF and DN.
# Latency
keywords: latencies in networks and data transfers, network latency
Latency is the time it takes for a data packet to travel from one point to another. There are two types of latency: network latency and data transfer latency. Network latency is the time it takes for a packet to travel across a network, and data transfer latency is the time it takes for a packet to travel from one point in memory to another.
Latency can be caused by many factors, including distance, congestion, and limited bandwidth. Latency can have an adverse impact on the quality of service (QoS) on any given network. In the case of the LTE network, measuring the impact of the E-UTRAN for this KPI: shall be the delivery of IP packets.
# Mobility
keywords: Measure the performance of the network, and movement of users and still retain the service
Mobility KPIs are used to measure the performance of a network that can handle the movement of users and still retain the service for the user, such as handover. This measurement should be used to observe the impact of mobility in E-UTRAN on end-users.
# Availability
keywords: availability KPI, 5G radio network, LTE radio network, 3G radio network
If the radio network is not available to the end user, even if it happens often that there is no availability, the end user. Hence, having a good radio network is vital from a business point of view This measurement assists the operator with information about the availability of the network operator’s radios. This measurement should be used to observe the impact of mobility in E-UTRAN on end-users.
# Utilization
keywords: utilization KPI, 5G radio network, LTE radio network, 3G radio network
The simultaneous utilization of network resources while also ensuring that the end-user experience is not interrupted.
Further readings:
3GPP TS 28.554 version 16.6.0 Release 16 – for 5G
3GPP TS 32.450 version 9.3.0 Release 9 – for LTE
3GPP TS 32.410 V17.0.0 (2022-04) – for UMTS and GSM
LTE Small Cell Optimization: 3GPP Evolution to Release 13
LTE Optimization Engineering Handbook, By Xincheng Zhang